-
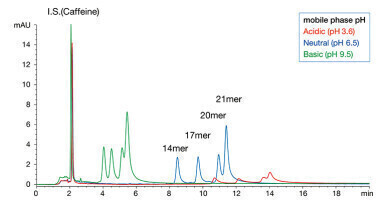 Figure 3: Influence of mobile phase pH on the separation of an all PO RNA mixture using an acidic (red), a neutral (blue) and basic pH (green).
Figure 3: Influence of mobile phase pH on the separation of an all PO RNA mixture using an acidic (red), a neutral (blue) and basic pH (green). -
 Figure 1: Determination of optimum method parameters for the analysis of oligonucleotides via HILIC
Figure 1: Determination of optimum method parameters for the analysis of oligonucleotides via HILIC
Liquid chromatography
Oligonucleotides in HILIC mode: Determination of optimum method parameters
Sep 26 2023
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) is an interesting alternative to anion exchange chromatography (AEX) and ion pair reversed phase liquid chromatography (IP-RP) for robust and highly sensitive UHPLC methods of oligonucleotides. Due to the highly polar nature of oligonucleotides, HILIC is ideally suited for their characterisation. In addition, it can be an advantage in some cases to employ an ion pair-free method.
In this technical note, the separation of mixtures of short DNA oligonucleotides (dT10, dT15 and dT20) and short RNA oligonucleotides (14, 17, 20 and 21mer) was used to examine important parameters for method optimisation in HILIC mode.
Influence of hardware
As observed for IP-RP mode, oligonucleotides also tend to interact with metallic surfaces of regular hardware in HILIC mode. Due to their electron-rich backbone, oligonucleotides can be irreversibly adsorbed onto the metallic surface of the column hardware. The use of bioinert column hardware such as bioinert coated YMC-Accura columns can mitigate this phenomenon. Consequently, the use of a YMC-Accura Triart Diol-HILIC column shows better peak shapes and higher sensitivity due to virtually no adsorption compared to the corresponding stainless steel column (see figure 2).
Influence of sample solvent
The influence of the sample solvent on peak shape especially for early eluting peaks is significant. As water is the strong eluent in HILIC mode, the ratio of organic solvent must be the same or higher than the initial gradient composition. The analysis of the DNA oligonucleotide mixture diluted with a low organic ratio (40%) compared to a sample solvent with high organic ratio (80%) shows that a higher injection peak as well as early eluting additional peaks occurs when the organic ratio is too low. Furthermore, the oligonucleotide peaks show broadening and the peak of dT10 even shows peak splitting. In comparison, by using a high organic ratio the peaks appear sharper and with higher sensitivity.
Influence of mobile phase pH
The mobile phase pH has a significant effect on retention and peak shape. Figure 3 shows the analysis of an all PO RNA mixture (14, 17, 20, 21mer) using a basic (9.5), a neutral (6.5) and an acidic mobile phase pH (3.6). The oligonucleotides are more strongly retained when the pH becomes lower. But with an acidic pH massive adsorption of the oligonucleotides occurs. For the 14mer the peak area is reduced by more than half compared to basic or neutral pH. Using the basic mobile phase, the retention is the lowest but the resolution is visibly reduced, so that the neutral mobile phase pH shows the best results for this mixture. In general, a neutral to basic mobile phase pH is recommendable for the HILIC analysis of oligonucleotides, depending on type and mixture.
Summary
These findings result in the following recommendations:
- Bioinert hardware provides optimum peak shapes and high recovery
- High organic ratio of the sample solvent is important
- Neutral to basic mobile phase pH is recommended
You will find further information about oligonucleotide analyses in YMC’s Oligonucleotide columns brochure.
Events
May 11 2025 Vienna, Austria
May 18 2025 Tempe. AZ, USA
May 21 2025 Birmingham, UK
Jun 01 2025 Baltimore, MD, USA
Jun 15 2025 Bruges, Belgium

















