Equipment
Proactively Tackling Unexpected Nitrosamine Contamination in Pharmaceuticals
Oct 22 2024
In recent years, the pharmaceutical industry has faced significant challenges due to the unexpected presence of nitrosamine contaminants in various medications. The issue first emerged in 2018 when an unknown impurity was detected in batches of the blood pressure medication valsartan. This impurity was later identified as the nitrosamine NDMA. The discovery prompted a series of investigations that uncovered additional nitrosamine contamination in other drugs, including the heartburn medication ranitidine and the diabetes treatment metformin. These findings led to multi-million dollar fines and reputational damage for the companies involved. Regulatory bodies like the EMA and FDA responded by mandating comprehensive risk assessments for nitrosamine contamination in all drug products.
Initially, the focus was on well-known small-molecule nitrosamines such as NDMA. However, it soon became apparent that a wider variety of nitrosamines were present in drug products. With nitrosamines potentially forming from the active pharmaceutical ingredients themselves, identifying what to look for became an increasingly complex challenge.
Many analytical methods at the time concentrated on targeted analysis of a predetermined list of compounds. This approach, while effective for known contaminants, left room for unexpected nitrosamine groups to go undetected. These could originate from nitrosamines forming in the final product due to interactions between ingredients not previously identified as risks or from contamination during the manufacturing process. If a nitrosamine wasn't on the testing list, there was a high chance it would remain unnoticed.
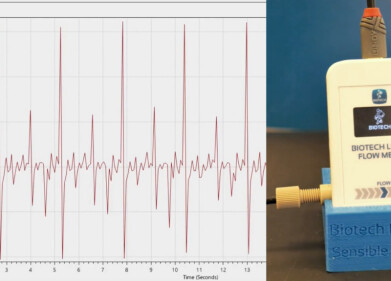
To address this issue, alternative strategies have been explored. One effective method is the Apparent Total Nitrosamine Content (ATNC) analysis. This non-targeted screening technique detects the nitrosamine functional group itself rather than specific nitrosamine molecules. By providing a single response for all nitrosamine content in a sample, ATNC analysis allows for rapid identification of potential contamination without needing to know exactly which nitrosamines are present.
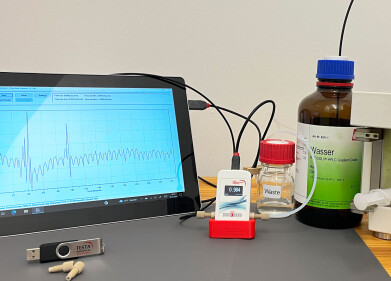
Ellutia's Automated Total Nitrosamine Analyser offers a robust solution to this challenge. It can quickly screen samples to confirm they are free of potential nitrosamine contamination down to parts-per-billion levels, without requiring standards for every specific nitrosamine. This enables users to focus detailed, specific testing only on samples that indicate possible contamination, making the testing process more efficient and comprehensive.
To find out more about how the Automated Total Nitrosamine Analyser works and how it can enhance nitrosamine testing protocols, visit the following link.
Events
Apr 27 2025 Portland, OR, USA
May 11 2025 Vienna, Austria
May 18 2025 Tempe. AZ, USA
May 21 2025 Birmingham, UK
Jun 01 2025 Baltimore, MD, USA