-
 Figure 5. Chromatogram of eye drop sample and absorbance spectra of Vitamin A standard and sample (fat soluble vitamins).
Figure 5. Chromatogram of eye drop sample and absorbance spectra of Vitamin A standard and sample (fat soluble vitamins). -
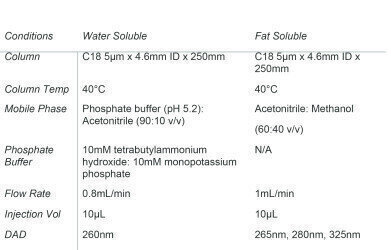 Table 1. Analytical conditions of the HPLC-DAD system for both water and fat soluble vitamins.
Table 1. Analytical conditions of the HPLC-DAD system for both water and fat soluble vitamins.
HPLC, UHPLC
The Analysis of Water and Fat Soluble Vitamins by HPLC-DAD
May 04 2020
Introduction
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is the standard routine method used during the analysis of vitamins. Vitamins are diverse compounds in structure, biological activities and chemical properties and are essential for normal metabolism function. They are naturally found in many foods but are also often added to processed food products and medications. Additionally, vitamin supplements are a growing trend among people whose diet is restricted. Vitamins are separated into two groups; water soluble and fat soluble. The most common water soluble vitamin supplements are Thiamine (B1), Pyridoxine (B6), Cyanocobalamin (B12), Riboflavin (B2), Niacin (B3), Nicotinamide, Ascorbic Glucoside, Vitamin C and Erythorbic Acid. The most common fat soluble vitamins are Retinol (Vitamin A), Retinol Acetate (Vitamin A Acetate), Ergocalciferol (D2), Cholecalciferol (D3), dl-α-tocopherol (Vitamin E), dl-α-tocopherol acetate (Vitamin E Acetate) and Phylloquinone (K1).
Routine analysis of vitamins can be challenging due to the unstable nature of the target analytes. Many factors can affect vitamin stability such as exposure to heat, light and air as well as interactions with other food components. By using reverse phase High Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with Diode Array Detection (DAD), two qualitative methods for the detection of water soluble and fat soluble vitamins was easily developed. For quantitative analysis, individual HPLC methods are recommended due to instability of various vitamins, in which decomposition regularly occurs during sample preparation.
This article details the analysis of both water and fat soluble vitamins by HPLC-DAD.
Experimental
A SCION 6000 HPLC with DAD was fitted with a 5µm C18 reverse phase column and used for the simultaneous identification of nine target water soluble compounds. Analytical standards were prepared with a range from 0.1mg/L to 50mg/L in tetrabutylammonium. For the analysis of Vitamin B1 and Vitamin B6, hydrochloride salt was used. One of the samples analysed was a nutritional supplement sample. Samples were diluted 1:10 before being filtered through a 0.45µm filter. Analytical conditions for the analysis of both water and fat soluble vitamins can be found in Table 1.
For the analysis of fat soluble vitamins, the same SCION HPLC-DAD was used for the simultaneous analysis of seven target analytes. Utilising the capability of the DAD to select multiple wavelengths, it was possible to identify all seven target analytes over three different wavelengths. Using varying wavelengths is vital, as fat soluble vitamins are often present at varying concentrations (main target vitamins and trace levels of other vitamins).
Analytical standards were prepared with a range from 0.01mg/L to 10mg/L for Vitamin A, 0.1mg/L to 100mg/L for Vitamin A Acetate, Vitamin D2, Vitamin D3 and Vitamin K1. The calibration range of Vitamin E and Vitamin E Acetate was 1mg/L to 1000mg/L. Methanol was used as a dilution solvent. One of the samples included a vitamin enriched, medicated eye drop sample. All samples were prepared with a 1:10 methanol dilution before being passed through a 0.2µm filter.
Results
To ensure good linearity, Vitamin C, Erythorbic Acid and Vitamin B12 must be prepared daily, due to the instability of the vitamins in the eluent. The linearity of the above vitamins were 0.996 or greater. Figure1 shows the linearity of Vitamin B6 which is representative of the remaining target compounds, all of which had a linearity value of 1.
Figure 2 shows the chromatogram of the 5mg/L water soluble analytical standard.
As shown in Figure 2, all vitamins exhibit excellent peak shape and are well separated. Figure 3 shows the chromatogram of the nutritional supplement sample.
The nutritional supplement sample contained four essential water soluble vitamins; Vitamin B1, Nicotinamide, Vitamin C and Vitamin B2. Using Compass CDS software, identification of target compounds is confirmed via absorbance spectrum comparisons. The absorbance spectra of the sample analyte is compared with the absorbance spectra of the same compound in the analytical standard, giving an extra level of confidence in the results.
The fat soluble vitamins exhibited excellent linearity for all seven target compounds, with an R2 value 0.9999 or greater. As represented by the excellent linearity, wide concentration ranges can be analysed on the SCION HPLC-Dad without the need for difficult sample preparation or method adjustments, even with unstable target compounds. Figure 4 shows the chromatogram of the analytical standard with the three difference wavelengths used.
Figure 5 details the chromatogram of the vitamin enriched medicated eye drop sample with the absorbance comparison spectra for Vitamin A (standard and sample).
As with the water soluble vitamins, Compass CDS was used for comparison of identified sample analytes and analytical standard components, via absorbance spectra comparisons. The two identified components of the eye drop sample was Vitamin A and Vitamin E Acetate.
Conclusion
Two different analyses for the simultaneous identification of nine water soluble vitamins and seven fat soluble was easily achieved using the SCION HPLC with Diode Array Detector. Sample preparation is a key factor that must be considered during these applications due to the unstable properties of the vitamins; especially Vitamin C and Erythorbic Acid. Utilising the multiple wavelength capability of the Diode Array Detector allowed simultaneous identification of fat soluble vitamins, with varying concentration ranges, over three different wavelengths. This eliminated the need for extensive sample preparation or numerous analytical methods. Excellent linearity was observed for all fifteen target compounds. Compass CDS software allows easy comparison of absorbance spectra for confirmation in identification.
More information online
Events
May 18 2025 Tempe. AZ, USA
May 21 2025 Birmingham, UK
Jun 01 2025 Baltimore, MD, USA
Jun 15 2025 Bruges, Belgium
Jul 14 2025 Kuala Lumpur, Malaylsia























