HPLC, UHPLC
The Importance of Mobile Phase pH in Chromatographic Separations
Sep 26 2023
In chromatography, the goal of method development is to achieve good separations with sharp, symmetrical, well-resolved peaks. The first step in method development is to begin with reasonable starting conditions, specifically the mobile phase pH. It is important to understand ionisation and the ionic form(s) of the analyte at a given pH to help determine the best separation conditions.
The Power of Mobile Phase pH
The pH of the mobile phase is a powerful tool that can control the factors governing chromatographic resolution, including separation efficiency, analyte retention, and separation selectivity. When selecting a desired pH, the dominant ionic form should be considered, as it is preferential to have all analytes in the same form (either ionised or unionised). Unionised analytes are preferred as they tend to have better retention than ionised analytes. Additionally, the hydrophobicity must be considered as retention time is longer for the more non-polar analytes. Predictive tools can be used to help determine the optimum mobile phase pH; ensuring method robustness and reproducibility.
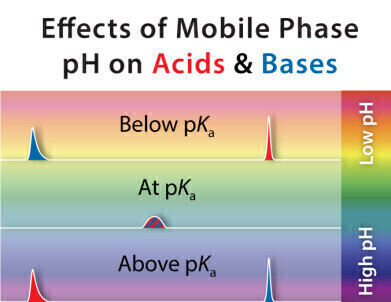
Effects of Variation in Mobile Phase pH
Selecting the most suitable pH for the analyte mixture is a crucial part of method development. It is necessary to investigate pH variation during method optimisation as small variations in pH can give rise to drastic changes in:
- Retention Time—As analyte ionization changes, so does retention behavior. Ionisable analytes are very sensitive to changes in mobile phase pH and slight changes in pH can lead to drastic changes in retention time.
- Peak Shape—Changes to the mobile phase pH affect the peak symmetry and width. When the mobile phase pH is too close to the analyte’s pKa, both species will be present in the sample, causing peak abnormalities (like peak splits/shoulders) to occur.
- Peak Spacing (Selectivity)—Variations in mobile phase pH can significantly affect the peak spacing between ionisable analytes. If the mobile phase pH is too close to the pKa, small changes in pH can have a huge effect on the separation selectivity, especially in the presence of similar structures.
Tight control of pH helps to separate closely eluting or overlapping peaks and minimises peak abnormalities. To maintain the desired optimum pH and fine-tune peak shape, consideration should be given to mobile phase parameters.
Using Prediction Tools to Ensure Separation Robustness
Taking a systematic, rational approach to method development can help prevent issues in retention behavior, selectivity, and peak shape. This involves recognising the extent to which the pH or pKa can be varied while still maintaining satisfactory analytical results.
Predictive tools in computer software like AutoChrom® or Method Selection Suite can help establish how much variation of mobile phase pH is possible, while still ensuring sufficient separation and resolution. These tools predict physicochemical properties (like pKa and logD) and simulate methods to determine optimum conditions. Use of predictive tools like these can help identify optimum conditions more quickly while building robustness into methods from the start.
Events
May 11 2025 Vienna, Austria
May 18 2025 Tempe. AZ, USA
May 21 2025 Birmingham, UK
Jun 01 2025 Baltimore, MD, USA
Jun 15 2025 Bruges, Belgium